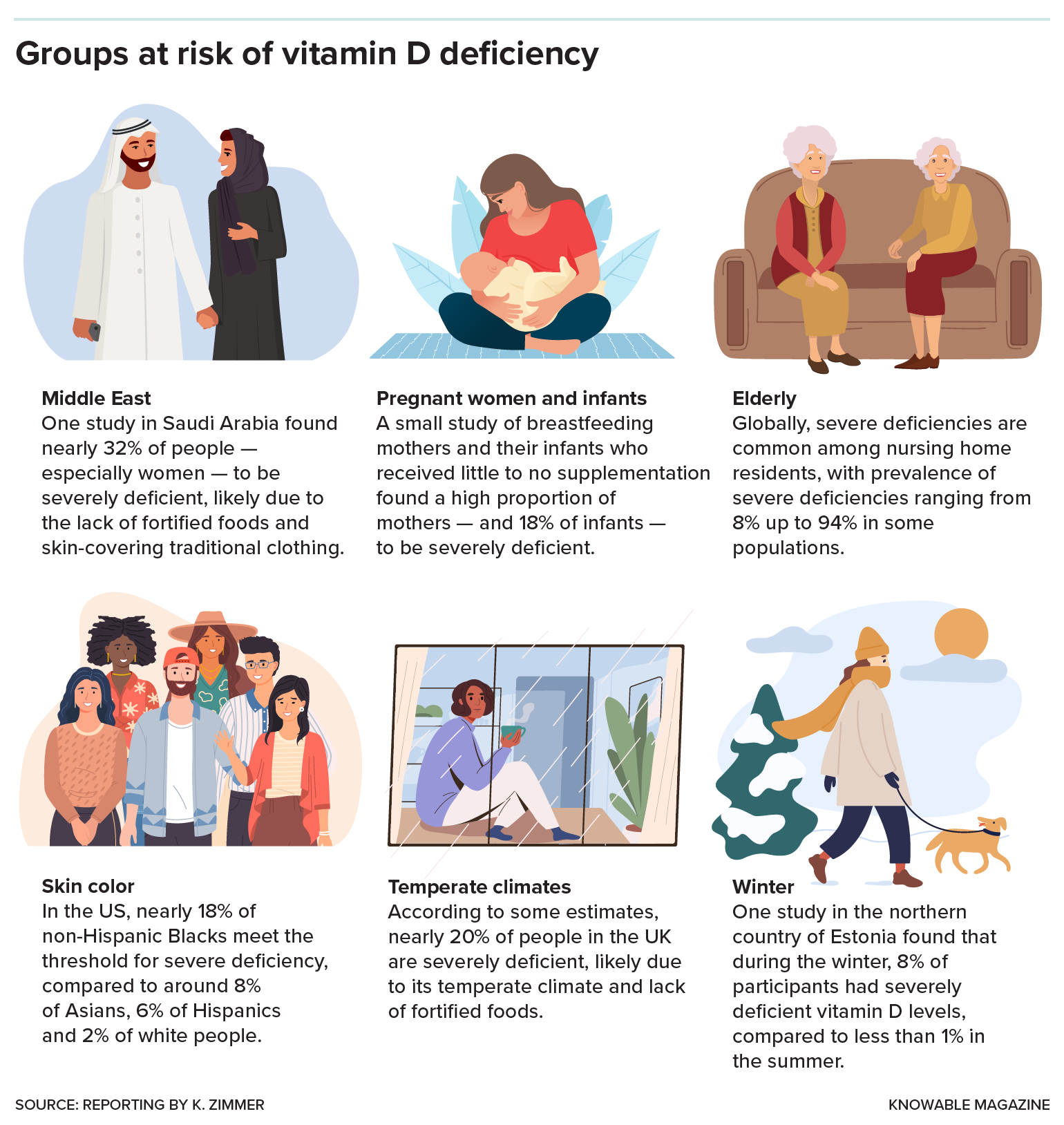
Certain groups of people are at greater risk of not getting enough vitamin D. Here are some of them.
Nutritional science is supposed to chart a course to our healthier selves. But contradictory scientific results and interpretations can muddy the waters — and few nutrients have recently demonstrated that more clearly than vitamin D.
At one point, it seemed that everyone should be taking vitamin D supplements, and that doing so would protect against a whole host of maladies, from bone problems to heart disease and cancer. More recently, new studies appear to have debunked many of those claims.
But a closer look at the research reveals a more nuanced message around vitamin D supplements: They can be key to correcting deficiencies, though people who already have enough — which is most of the American public — are generally unlikely to see benefits from taking large doses. Experts have come to worry about supplement enthusiasts overdosing in the belief that more is better or, at the other extreme, some nutrient-deprived people shunning them altogether.
Ultimately, says Roger Bouillon, an endocrinologist at KU Leuven in Belgium, “it’s like for most things. You need an optimal amount: not too little, not too much.”
Yet working out who needs vitamin D supplements, how much, and what the specific health benefits are, remains tricky, with questions remaining. Here’s some of what we know.
What does vitamin D do, and where does it come from?
The importance of vitamin D came to light at the start of the Industrial Revolution in the late 1700s, when people in northern climes crowded in dark, polluted cities and spent more time working indoors. The majority of children in cities like Boston developed rickets, wherein bones soften, weaken and often deform.
Scientists eventually discovered that exposure to sunlight would cure and prevent the disease.
Later, researchers learned that UV light from the Sun kick-starts a reaction that generates vitamin D. The vitamin gets converted into its active form in the kidneys and then is shuttled to the intestine, where it stimulates cells to move calcium, a key building block of bones, into the bloodstream. “The most important thing vitamin D does is intestinal calcium absorption,” says Sylvia Christakos, a biochemist at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School.
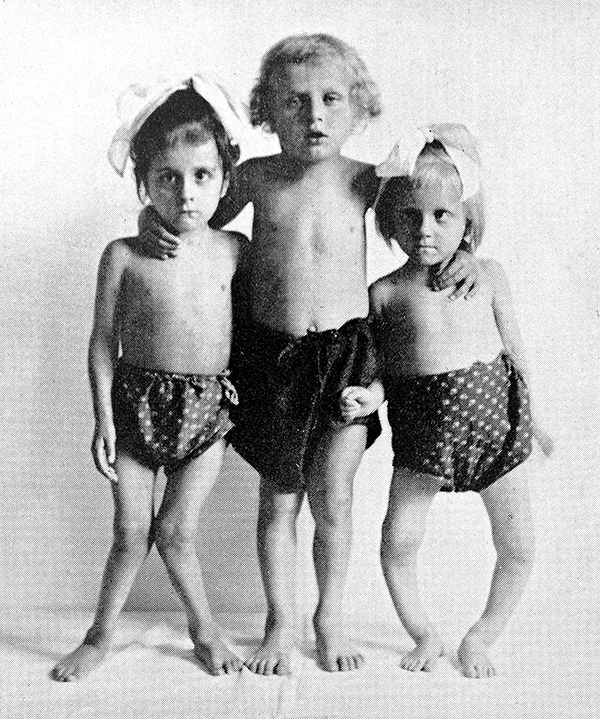 Severe vitamin D deficiency can cause the disease known as rickets, in which a lack of calcium leads to bone deformities. The disease was common among children in dark, northern cities before the discovery of vitamin D.
Severe vitamin D deficiency can cause the disease known as rickets, in which a lack of calcium leads to bone deformities. The disease was common among children in dark, northern cities before the discovery of vitamin D.
CREDIT: WELLCOME COLLECTION
Though the effects are most severe in children, vitamin D deficiencies can also cause a softening of adult bones called osteomalacia, and increase the risk of osteoporosis, where bones become weak, brittle and more prone to fractures. Though experts debate what exactly constitutes a vitamin D deficiency — and know that healthy levels may vary from person to person — everyone agrees that blood levels should not go below 12 nanograms per milliliter to avoid severe deficiency.
Such severe deficiencies — and the bone ailments they cause — are still rampant across the world. Surprisingly, more than 30 percent of people in some sunny Middle Eastern countries are severely deficient, which may be partly attributed to skin-covering traditional clothing. By contrast, in Finland, a sun-deprived country with dark winters, severe deficiencies are relatively rare, thanks to government policies to fortify dairy products with extra vitamin D.
In contrast, around 20 percent of the United Kingdom’s population is severely deficient by some estimates, due to its northern, cloudy weather and a lack of fortified foods. The United States, where many dairy products, and some juices and breakfast cereals, are fortified, falls somewhere in the middle: Around 6 percent of people are severely deficient. “For the most part in the US, we don’t see frank nutrient deficiencies,” says Regan Bailey, a nutrition expert at Texas A&M University who recently coauthored a review on supplement use among the public in the Annual Review of Nutrition. (Some research groups have produced much larger deficiency estimates by using blood level thresholds that many experts say are too high to qualify as nutrient deficiencies.)
Since 2010, the National Academy of Medicine has recommended relatively modest daily doses: 400 international units (IUs) for babies, 600 IUs for everyone up to age 70 and 800 IUs for older people. These doses are designed to achieve levels of 20 nanograms per milliliter — more than enough to avoid severe deficiencies — for otherwise healthy people in the United States.
Most people should be able to get these doses through brief sun exposure, says John Christopher Gallagher, an endocrinologist at Creighton University in Omaha, Nebraska. Measuring vitamin D production in the skin is not an exact science, but five to 10 minutes’ daily exposure without sunblock of just the face, neck, hands and arms should do the trick in the sunnier months, even in temperate places like Boston. While it’s entirely possible to get enough vitamin D this way, the official stance of the American Academy of Dermatology is to not get vitamin D from sun exposure.
Fortified dairy products and other foods will also provide enough.
Foods that naturally contain vitamin D, such as fatty fish, egg yolks, red meat, liver and irradiated or sun-dried mushrooms, which are especially rich in vitamin D due to their increased exposure to UV light, can also help. “If you’re out and about and you have sun exposure during some months of the year,” Gallagher says, “you probably get plenty of vitamin D.” That’s especially true if you have enough dairy in your diet.
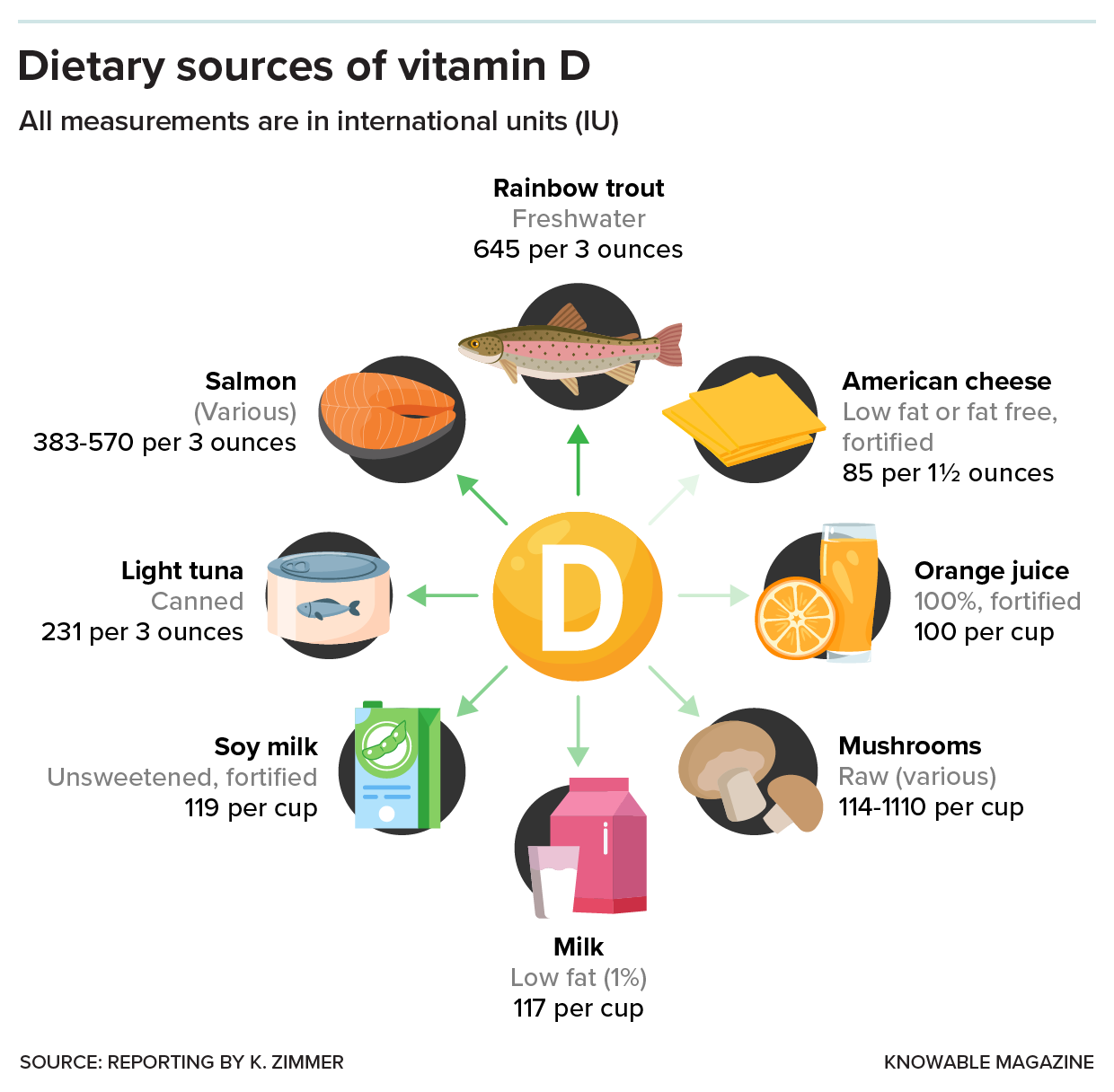
A few common food items can deliver a significant portion of your daily vitamin D needs, either because they are naturally rich in it or because they are fortified with the vitamin.
Does anyone need supplements?
Generally, people need supplements only when they’re not likely to get enough from natural or dietary sources, health experts say. Deficiency-prone populations include breastfed infants who don’t get fortified formula, elderly people (whose skin makes vitamin D less efficiently) and pregnant women.
People with dark skin tones should also take care to get sufficient vitamin D, because melanin pigmentation in the skin blocks UV light.
People in northern latitudes like England “should all take a supplement during the winter,” adds nutritional scientist Susan Lanham-New of the University of Surrey in the UK, although that’s less important in places like the United States that have food fortification.
Experts worry that it’s often the people already getting enough vitamin D through diet and lifestyle who are the most likely to take supplements, Christakos notes. Meanwhile, communities who need vitamin D supplements the most might not realize their need and may have read news reports suggesting that the supplements aren’t necessary.
That’s an especially dangerous message in countries where deficiencies are common — for instance in the UK, where physicians still see children with deficiency-related ailments, says Martin Hewison, a molecular endocrinologist at the University of Birmingham in that country. One of his UK colleagues is struggling to persuade some of her vitamin D-deficient patients to take supplements because they believe it is a waste of time.
For anyone concerned that they’re not getting enough vitamin D, experts say that up to 1,000 IUs a day would more than suffice. If possible, Lanham-New adds, make sure it’s vitamin D3, a version typically extracted from sheep wool that appears to be better at raising vitamin D blood levels than D2, which is often vegan and mushroom-based.
But avoid the high doses — of 5,000, 10,000 or 20,000 IUs, or even higher — that can be found in drugstores or online, stresses JoAnn Manson, an endocrinologist and epidemiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School. Too much vitamin D, even when taken occasionally, can sometimes cause bone health to deteriorate and lead to an overdose of calcium in the blood and urine, resulting in nausea and even kidney failure. There are reports of people in the UK and US ending up in the hospital after taking excessive doses.
Some experts have advised that Black Americans, in particular, take higher doses of supplements — for instance, 2,500 IUs — as they’re especially prone to low levels. But here’s a mystery: Even though 17.5 percent of African Americans have deficient levels of vitamin D, those vitamin-deficient Blacks tend to have better bone health than comparably deficient Caucasians, notes biomedical scientist LaVerne Brown of the National Institutes of Health. It’s possible, she says, that African Americans need less vitamin D than other populations, perhaps because they’re better at metabolizing vitamin D to its final active form. If that’s true, then high doses may have a greater risk of causing harm in African Americans.
“We just don’t have the studies that are focusing on these populations in order to come up with definitive answers,” Brown says. In the meantime, an expert panel meeting in 2017 concluded that the current recommended intake should be enough for African Americans, the same as everyone else. “Anything above 800 IU, it’s not clear that there’s a real need for that,” Brown says.
Could higher doses have benefits?
More than two decades ago, scientists began to make observations suggesting that vitamin D at higher doses could have benefits beyond bone health. Dozens of studies described strong correlations between people’s vitamin D levels and a range of diseases like cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes and certain cancers. The lower someone’s vitamin D levels were, the likelier they were to have these diseases, while higher levels were associated with being healthier.
Other research showed that many cell types — in the lungs, heart and immune system — have receptors for the vitamin to dock onto, hinting at far-reaching effects across the body. Giving vitamin D to lab mice with conditions mimicking human diseases could often improve their ailments. Vitamin D, it seemed, might help to tackle the major diseases of our time.
From New Zealand to Europe to North America, scientists launched large clinical trials, enrolling thousands of people over multiple years, to test whether vitamin D supplements would decrease their risk of disease. Importantly, the studies focused on members of the general public, who were largely healthy and had adequate levels of vitamin D. These people then received relatively large doses, of 2,000 or 4,000 IUs or even higher. The studies asked whether there were benefits from getting more than the recommended dietary allowance and ending up with blood levels even higher than 20 or 30 nanograms per milliliter, Manson explains.
To the disappointment of many scientists, giving these generous doses to healthy people didn’t change their risk of developing cancer, heart disease or asthma, nor did it significantly prevent the progression to type 2 diabetes. Extra vitamin D beyond the recommended levels didn’t even do anything to improve bone health or reduce the risk of fractures.
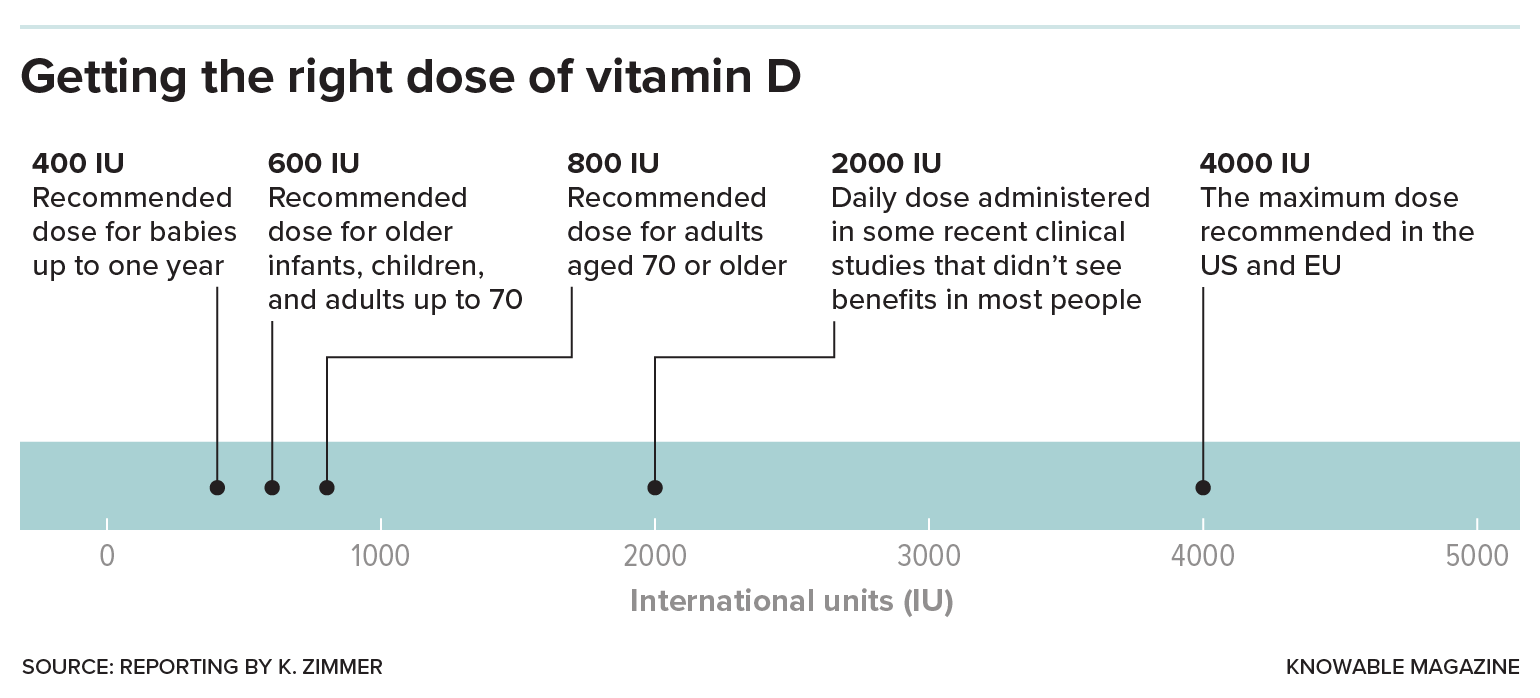
Experts recommend relatively modest daily doses of vitamin D supplements.
There may be a simple biological reason why more vitamin D isn’t necessarily better: The version of vitamin D found in supplements needs to be converted in the liver and kidneys to reach its final, active form — and that process is probably tightly controlled, says Bouillon. “The body regulates that so you have the exact amount, and not more than what you need.”
The takeaway, many experts agree, is that most healthy people aren’t going to benefit from high doses of vitamin D if they already have enough. The tantalizing associations that led researchers to suspect additional powers of vitamin D could have been an illusion: People with illnesses may end up with lower vitamin D levels because of the diseases themselves, or the unhealthy lifestyles that caused them, says Bouillon.
Are larger doses ever helpful?
A few of the recent trials hinted that some groups of people may benefit from higher doses, but these possible benefits need to be confirmed in further studies, says Manson, who ran one of the trials, called VITAL, which studied nearly 26,000 US adults over five years and looked at supplements of 2,000 IUs of vitamin D as well as omega-3 fatty acids. In that study, participants didn’t have a lower risk of developing cancer but they did have a 25 percent lower chance of it metastasizing or becoming fatal. Perhaps, says Manson, vitamin D makes tumors less likely to metastasize and kill. VITAL also reported that high doses of vitamin D made people less likely to develop certain autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis and lupus.
Manson notes that these benefits appeared to be most visible among people with a healthy weight, compared to overweight or obese participants. But she cautions that more research is needed to understand these observations and confirm the observed benefits of larger doses.
Physicians in clinical practice, of course, have leeway in prescribing higher doses to certain people as they see fit, such as for osteoporosis patients, or people with conditions that hamper the absorption of vitamin D through the diet, like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
What don’t we know yet?
As they probe potential effects of higher doses in non-deficient people, researchers still don’t know how many roles vitamin D might have. The trouble is that recent trials don’t tell us whether having enough vitamin D is important for maintaining healthy heart function or avoiding cancer, for instance — only that having more than that won’t help in most cases.
To prove that adequate vitamin D has health benefits beyond keeping bones strong, scientists need more research in which some deficient people receive supplements and the rest receive a placebo. But such studies are hard to conduct in places like the US, where severe deficiencies are relatively rare. It’s also not ethically justifiable to seek out people who are deficient and then deprive half of them of much-needed supplements, because of the risk of poor bone health in vitamin D-deficient people.
Some scientists believe that having enough vitamin D could be key to maintaining heart and immune system health and preventing diabetes and cancer — and perhaps even be important for brain function, athletic performance and other claims. The evidence is particularly strong in the immune system, says Hewison, whose research points to key roles of vitamin D in immune cells; and indeed, human trials that by chance included some deficient people show benefits of supplementation in warding off infections.
But there just aren’t enough data yet, Hewison says. “I think this is the issue facing the field as a whole.”
Katarina Zimmer is a science and environment journalist and a contributing writer to Knowable Magazine. Check out more of her work at www.katarinazimmer.com.
This article originally appeared in Knowable Magazine, a nonprofit publication dedicated to making scientific knowledge accessible to all.
